World News

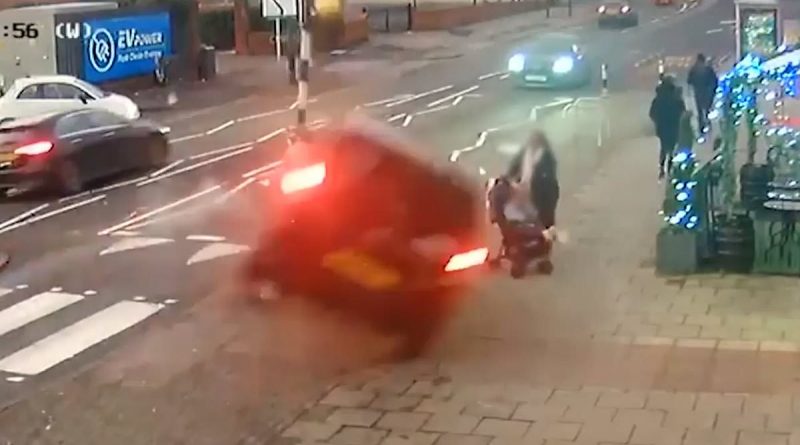
BBC 'trivialise' moment car nearly crushed mother and child in crash
West Midlands mayor accuses BBC of ‘trivialising’ moment car nearly crushed mother and child in crash with ‘inappropriately light-hearted’ coverage
Blockchain
Blockchain Expert Likens Crypto to Early 20th Century U.S. Stock Market
On 18 December 2023, Jamie Coutts, a freelance blockchain strategist and former crypto market analyst at Bloomberg Intelligence, shared insights
Crypto
How to make passive income on crypto
Blockchain technology is changing the world. These days, we see how many breakthroughs in different areas have been made thanks
Politics

Government borrowing higher than expected at over £200 a head as cost of bene…
Ministers borrowed around £213 per person last month amid greater benefits costs and increased interest payments, official figures have suggested.
Business And Finance

Microsoft Accidentally Exposes Xbox Crypto Wallet Roadmap in FTC Case
In an information that has been called the “biggest in Xbox history,” tech behemoth Microsoft has inadvertently revealed plans to





























