2021 Market Risk Analysis Report
Coronavirus and the way to recovery
One year has passed since the outbreak of the Covid-19 and we can still see major challenges even today. The deadly virus affects many people daily lives, but the most serious impact is the economic development of global economies.
To effectively fight infectious diseases, many countries adopted a lockdown policy, and many companies were forced to follow a work-from-home policy.
That means, many products were unable to be completed on time and exports cannot proceed smoothly, as global supply chains been disrupted.
These effects will be directly reflected in the country’s GDP. In this case, not only does the data reflect a pessimistic attitude towards the US economy, but the number of cases is increasing rapidly every day, which makes investors infinitely pessimistic about the long-term economy growth.
COVID-19 impact in the United States is more serious, and there is no signs of slowing down. Therefore, at that time, currencies fell sharply in countries with a single-day surge of new cases.
On the other hand, a country’s progress in controlling the spread of epidemics can usually support a strong currency.
Wuhan City and Hubei Province were almost completely shut down for a month, and domestic and international air travel was severely restricted. Chinese economy rebounds, the US economy was hit by the second wave of COVID-19.
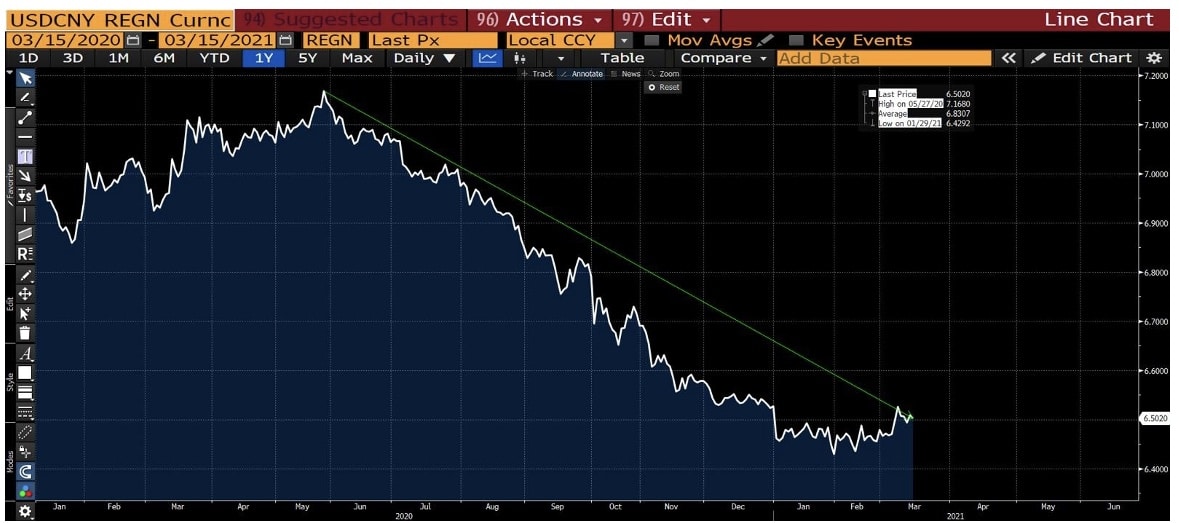
Currently, COVID-19 is under control in China, but is still spreading in the United States, helping the yuan to rebound strongly from July to September.
The exchange rate of RMB against the US dollar rose from 7.16 yuan/US dollar at the end of May to 6.75 yuan/US dollar at the end of September 2020. As a result, Yuan increase of approximately 6%.
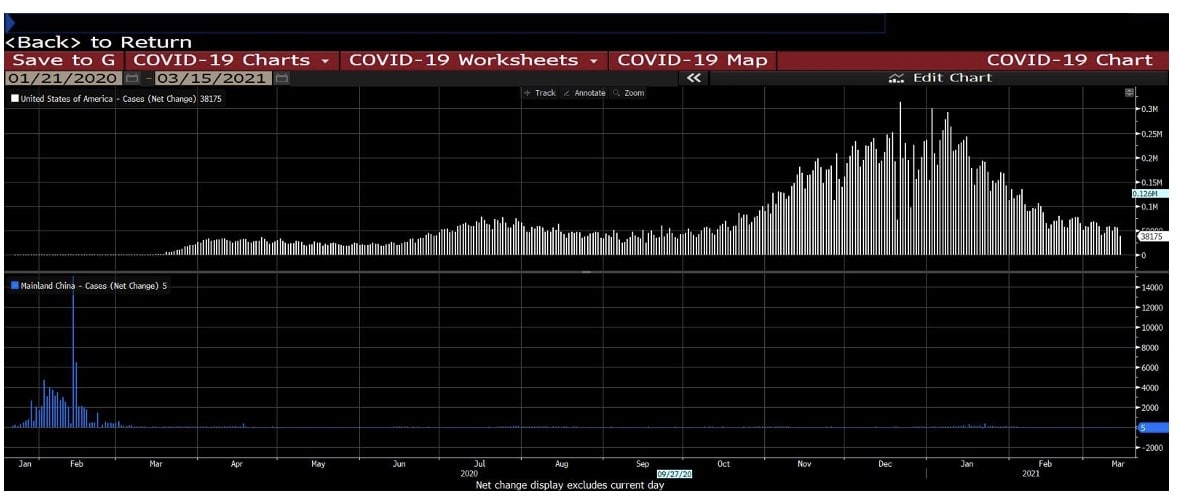
Turning to EURUSD, when the epidemic started, the euro weakened against the dollar. Before the virus entered the United States, Europe, especially Italy, was severely hit.
Since then, the situation has changed. From the low of March 20, to the end of August, the exchange rate of the euro against the dollar has risen by more than 10%.
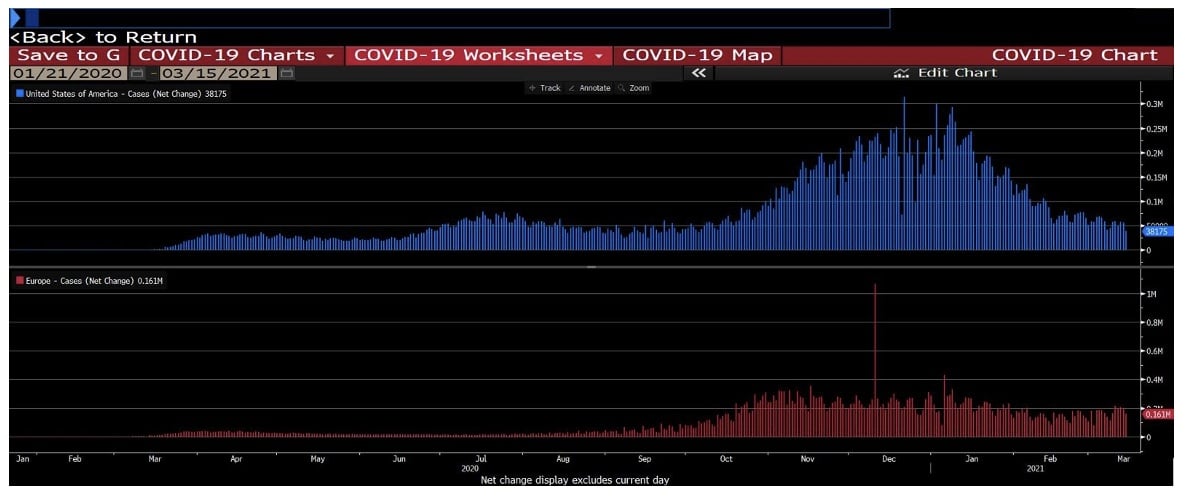
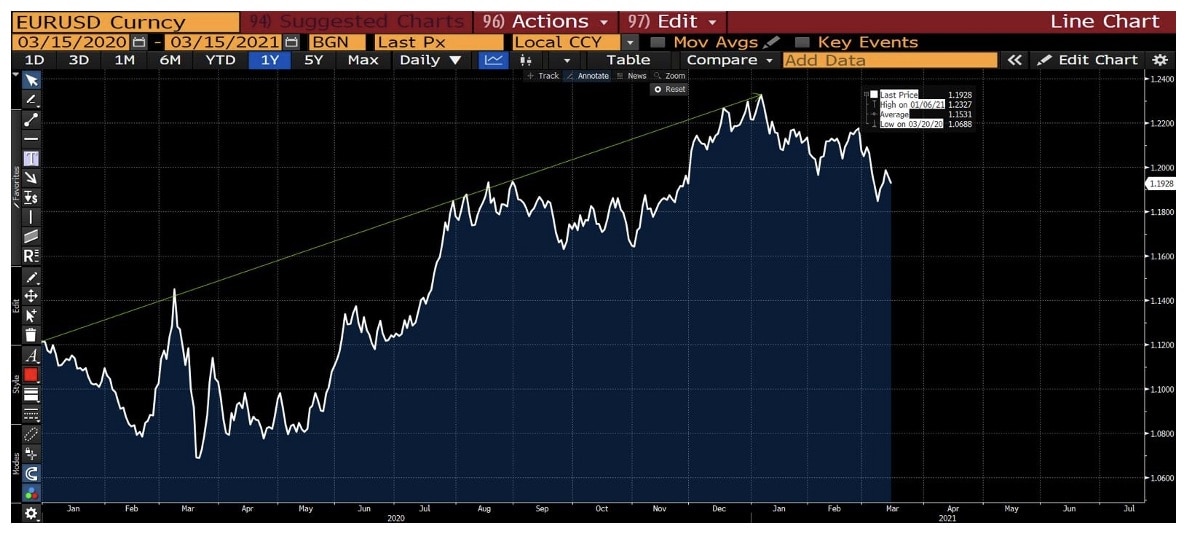
Recently, with the advent of vaccines and lower number of cases, global investors have begun to adopt an optimistic attitude towards the capital market and have begun to re-enter the market.
In addition, particularly in the United States, the government has implemented some stimulus plans in order to speed up the economic recovery.
Interest Rates
In support of the US economy and financial markets, the US Fed has cut its benchmark interest rate to a range of 0% to 0.25%.
The most fundamental method to decrease the federal fund rates is to start purchasing US government securities from Federal Reserve member banks.
As a result, the banks end up holding fewer securities and more cash reserves, which they can lend out in the federal funds market to other banks.
That increase in the supply of available reserves causes the federal funds rate to decrease. By bringing down the federal fund rate, the domino effect leads to lower a cost of short-term loans than that of long-term loans, such as mortgages, home loans, and bank loans.
In short, the purpose of a low interest rate can potentially stimulate economic growth during a period of economic recession and decline; simply, it means that borrowing costs become cheaper.
A low interest rate environment not only can spur demand for household goods, but also benefit financial institutions, being able to lend more.
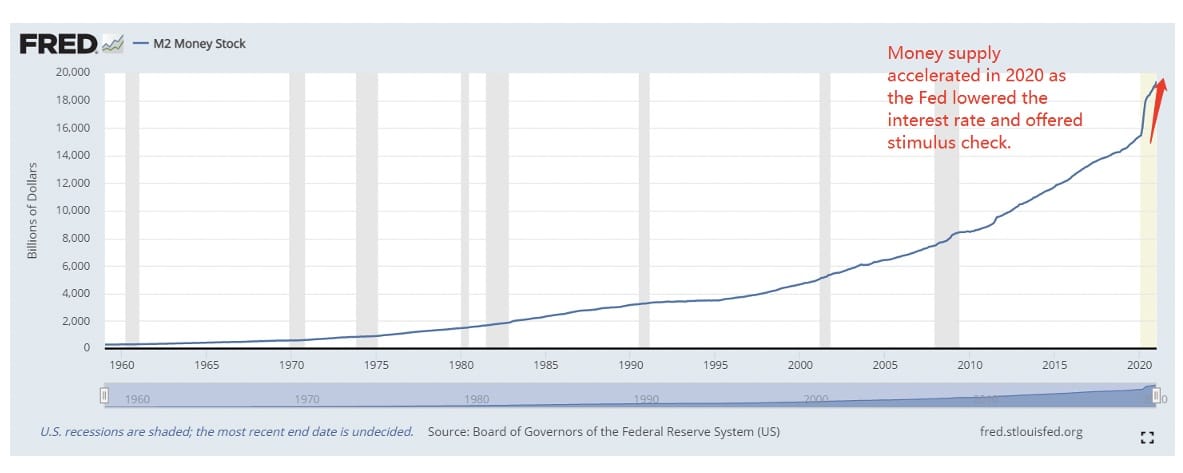
Money Stock
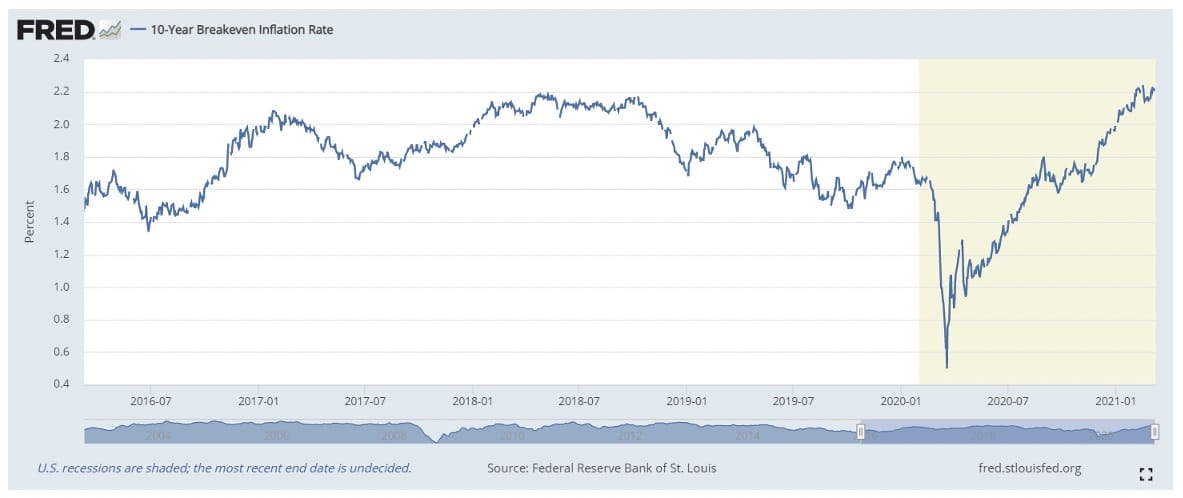
10- year Breakeven Inflation Rate
According to the most recent Fed meeting, the central bank so far has no plans to raise interest rates as the economy is still a long way from the Fed’s goals. Powell said that Interest rates will stay unchanged until early 2023. However, as the economy appears to be recovering faster than expected, Atlanta Fed President, Raphael Bostic implied that interest rates might rise sooner than early 2023, and potentially could be as soon as mid-2022.
Short- run Philips Curve
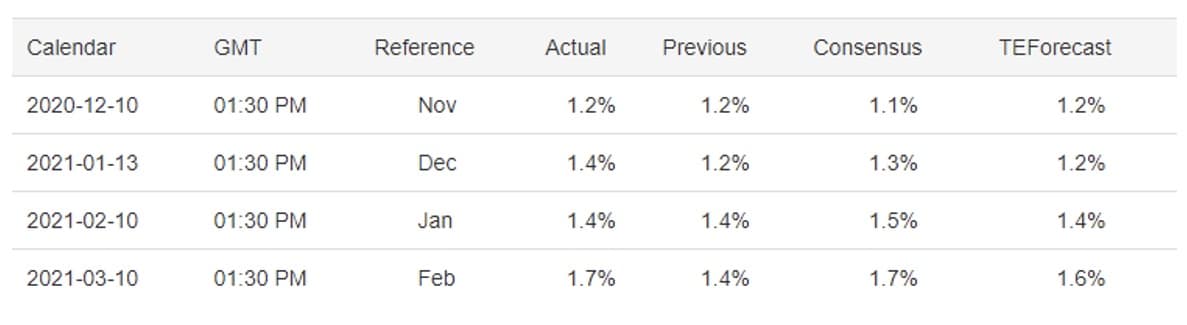
US Inflation Rate
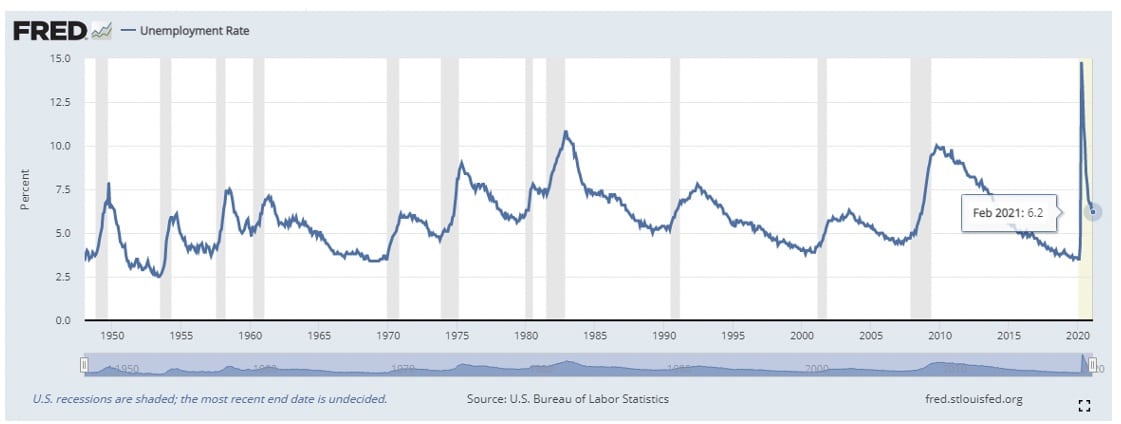
US Unemployment Rate
Staying with the unemployment rate issue, prior to March 2020, the last time the Fed reduced interest rates to near zero was December 2008, when the Great Recession happened; then the rates remained unchanged until December 2015. As the diagrams shown below, the Fed left the rates near zero until the unemployment rates declined to around 5%.
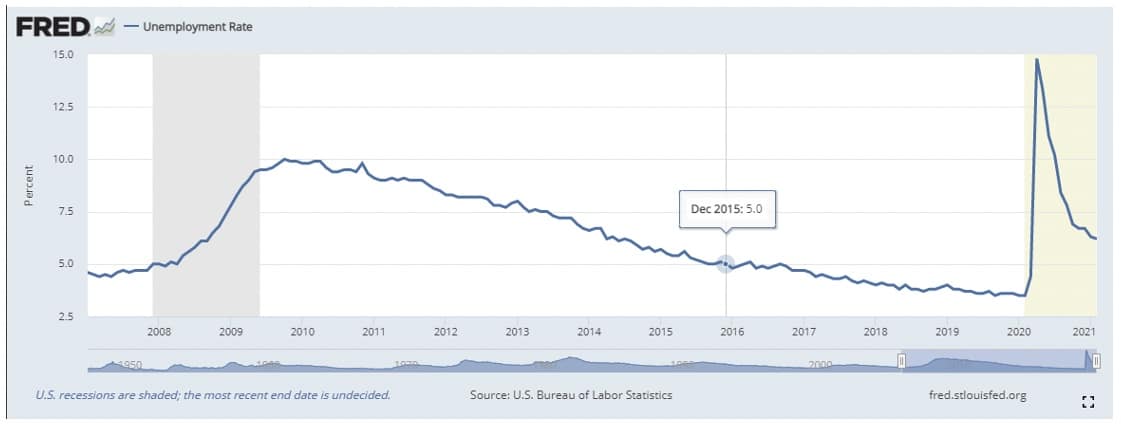
Unemployment Rate
To use the previous example as a reference, it is foreseeable that that federal fund rate will remain unchanged at least through 2022, or later as the projection for a below 5% unemployment rate will not occur before then.
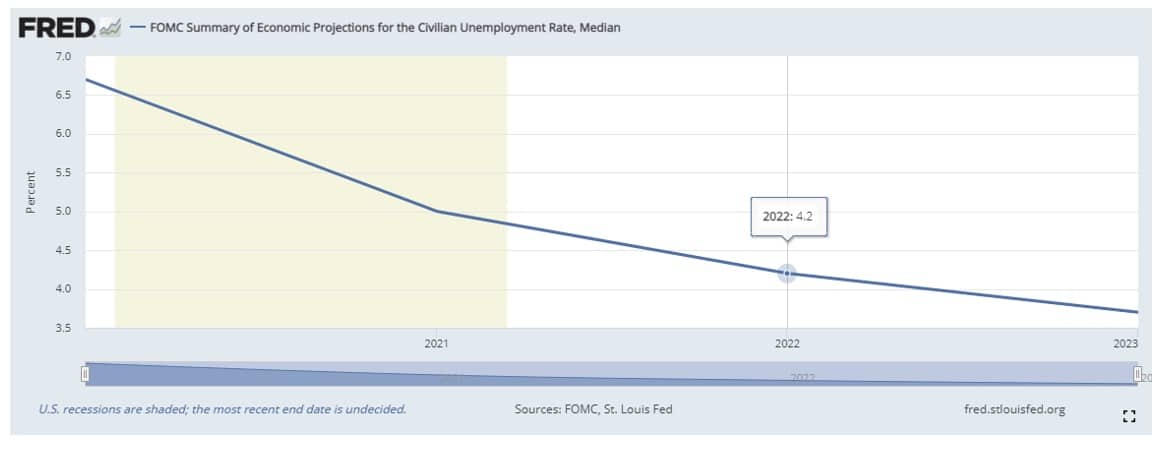
Projection for unemployment rate
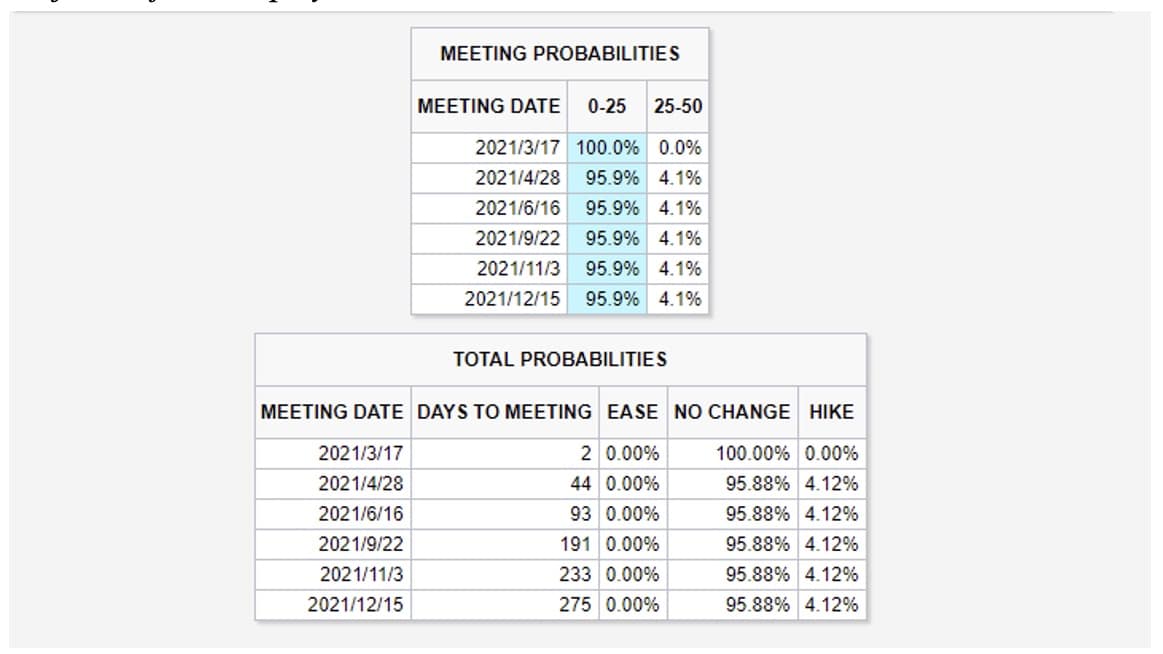
Probability outcome for the Fed rates
2021 Bond Yield and Dollar Weakness
The first three months of 2021 were rather chaotic for the bond market. Up until March 9th, the 10-year treasury yield had appreciated beyond 70%. In convention, when rates in the long end of the yield curve rise, the equity market would experience a correction.
That does not appear to be the case in 2021, the Dow Jones Industrial Index refreshed record highs as yields climbed back to pre-pandemic levels. Some investors speculate the stock market was mounting toward a bubble.
The key piece to answering the above abnormality lies within the US repo market, where large institutional banks borrow and lend to each other.
Quoting from Yahoo Finance, “The cost of borrowing U.S. 10-year notes went negative last week (as in week of March 1st) in the repo market following a surge in short positioning on U.S. 10-year notes as expectations have grown for a faster-than-expected U.S. recovery.”
Borrowers in the money market are required to put high-quality securities upfront, such as the 10-year government bond, as collateral to the lenders. With negative repo rates, lenders are willing to inversely pay interest to borrowers to collect their bond collaterals.
Looking at the M2 money supply in figure 1, one could easily spot the Fed’s liquidity providing far outpacing ECB since last March, where the pandemic hit global equity markets. The bigger spending has a tremendous effect in restoring investors’ confidence.
As shown in figure 2, the S&P 500 index plunged alone with the Stoxx 600 index but recovered far quicker thanks to the Fed’s generous support.
The S&P index has been outperforming its peers up until today, the higher return in the equity market attracts foreign demand, thus will bolster the US greenback.
Better vaccination rollouts also contributed to stock outperformance as investors expect a faster reopening of the US economy. Doses of Covid-19 vaccine administered in the US were doubled that of its counterpart. (figure 3)
The lack of a dominant factor puts more fog into the picture, as of now it would be hard to determine whether the shared currency will have the upper hand over the US greenback in 2021.
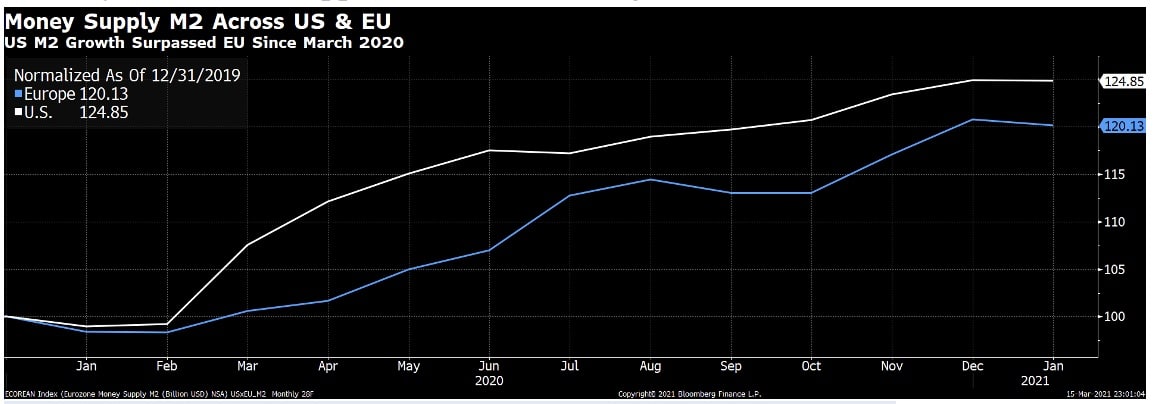
Figure 1, M2 increased by 25% in the US compared to 20% in EU
The Sterling was underpinned by strong fundamentals, such as the locked-in Brexit deal and a more coordinated vaccination campaign. Cable appreciated as much as 6% this year after UK shrugged-off cloudy Brexit headlines.
The UK is now free to set its trade policy, which opens the door to better deals with the US, Australia, New Zealand, and China.
In the southern hemisphere, Aussie and Kiwi enjoyed a nice ride on the ‘reflation trade’. Commodity demands are picking up from rebooting manufacturing and industrial sectors.
Safe-haven currencies like the Japanese Yen and Swiss Franc will be on the back foot against the US greenback amid rising and stabilizing bond yields. Widely received vaccinations will eventually create herd immunization, and the fear of the coronavirus will be left behind.
Potential Trade Wars and Their Implications
Sino-American Trade War
Brief:
All started with the former US president Trump’ accusation of China practicing unfair trading and intellectual property theft. On the other hand, from the perspective of the Chinese government, they believed that America was trying to impose tariffs to curb its rise as a global economic power.
Results:
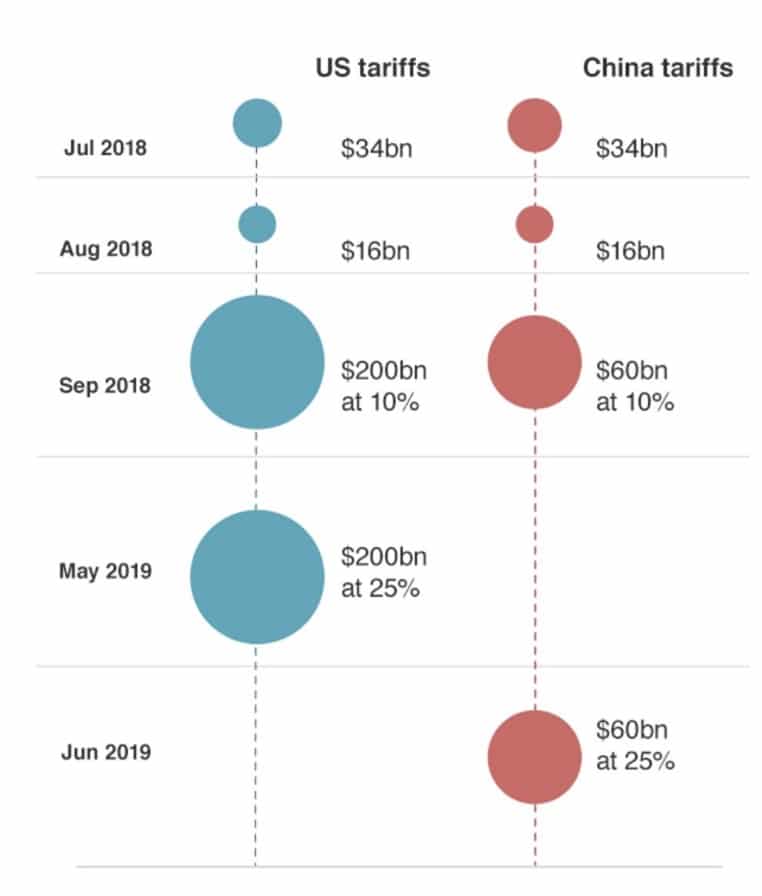
Currently, under the “phase one” deal that was signed in Jan 2020, China promised to boost US imports by $200 billion, above the 2017 levels and strengthened intellectual property rules.
Even though the former U.S. president Trump has stepped down, it is unclear if the Biden administration would try to pressure China with more tariffs or if the two economic powers would figure out other ways to settle the disputes.
Analysis
Even though the two trade wars posed significant challenges to the businesses that operate in China, the European zone, and the U.S., it appears that the impacts of the announcement for trade wars did not strike the forex markets, particularly the DXY, that much.
In conclusion, both trade wars were initiated by the U.S. former President Trump and his administration, so it is not prudent to believe that a less aggressive Biden government would keep on with the trade war proposals.
Although we can never rule out the possibilities of trade war resumptions, we can still rest assured knowing that the U.S. imposed trade wars against Euro and China did not pose significant challenges to the forex market in previous years.
Source: Read Full Article

